CONVERGENCE ANALYSIS.
Convergence analysis is an interdisciplinary approach that examines how different sectors, disciplines, and systems can align to address complex challenges. In healthcare, this concept involves integrating data, methodologies, and strategies from diverse fields to develop comprehensive solutions. Convergence analysis is particularly valuable in addressing health equity issues, as it enables a holistic understanding of the social determinants of health (SDOH)—factors like education, housing, employment, and access to healthcare that influence health outcomes.
Chronic Disease by County Maps
Applying Convergence Analysis to Promote Health Equity.
Identifying Systemic Inequities
Convergence analysis allows researchers and policymakers to combine data from various sources, such as census data, electronic health records (EHRs), and social service reports, to identify patterns of health disparities. For example, geographic information systems (GIS) can be integrated with public health data to map areas with limited access to nutritious food or healthcare facilities. This multi-source approach identifies root causes of inequities, such as residential segregation or economic disparities, that disproportionately affect marginalized populations.
Designing Targeted Interventions
Through convergence analysis, stakeholders can create interventions tailored to the specific needs of communities. For example, combining behavioral health data with housing statistics might reveal that residents in low-income areas face higher rates of mental health issues due to housing instability. Addressing these interconnected issues through coordinated housing policies and mental health services promotes equity.
Facilitating Cross-Sector Collaboration
Convergence analysis emphasizes the interdependence of various sectors in improving health outcomes. In promoting health equity, it facilitates partnerships between healthcare providers, educational institutions, and social services. For instance, hospitals could partner with local food banks and schools to implement programs addressing food insecurity and its impact on children’s health and educational outcomes.
Evaluating Policy Impact
By integrating diverse data sets and perspectives, convergence analysis enhances the evaluation of policies and programs aimed at reducing health disparities. For example, linking Medicaid data with transportation statistics can assess whether improved public transit access enhances healthcare utilization among underserved populations.
Empowering Community Engagement
Convergence analysis prioritizes the inclusion of community voices, ensuring that interventions are culturally and contextually appropriate. Engaging communities in the data-gathering process allows researchers to identify overlooked SDOH and empowers residents to advocate for systemic changes.
Visualizing Convergence Analysis.
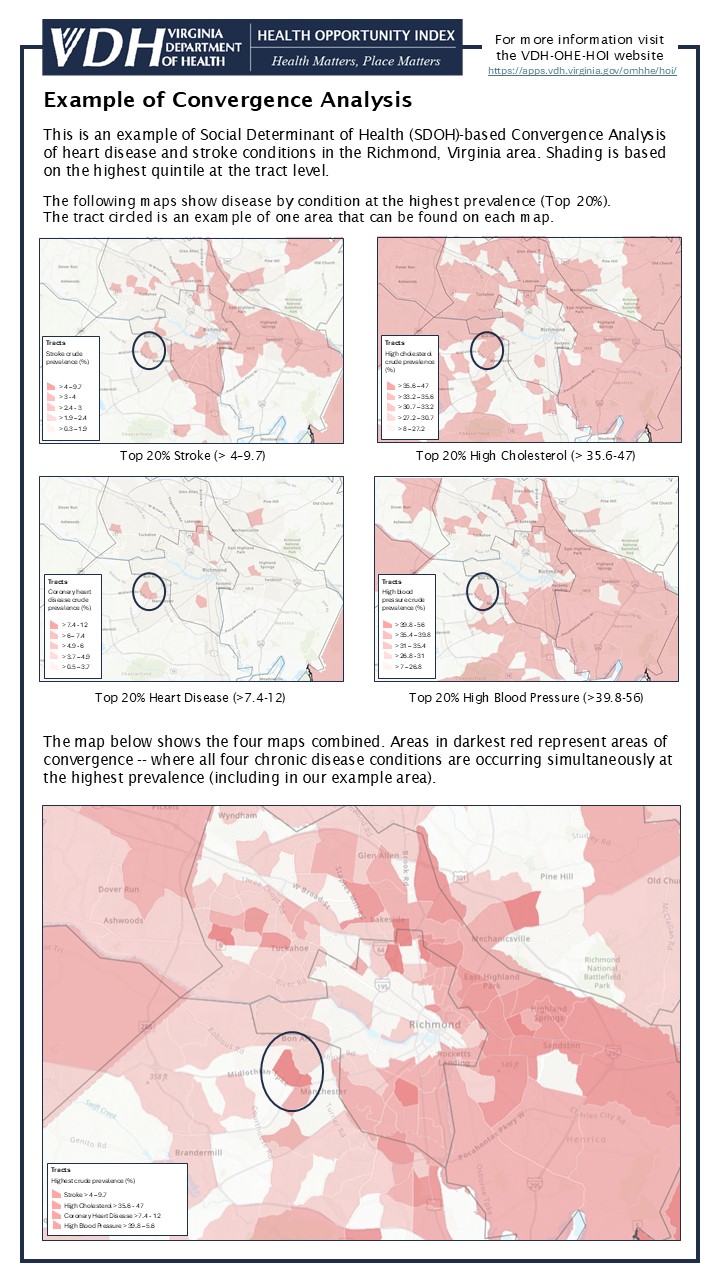
The following is a simple example of convergence analysis visualized using one data source (CDC PLACES 2002 data) and four variables. Convergence analysis can incorporate a virtually unlimited set of variables from multiple sources so long as all of those variables are reported at the same geographic level (i.e. Census tract or county) to show where populations in a market might be experiencing poor outcomes.